Acupuncture and Nutrition For Relieving Joint Pain
Many people are not aware that in most TCM schools Eastern and Western nutrition is a required class. This is important because diet and lifestyle has a great effect on the body. Remember in TCM we look at the whole picture. When I conduct an intake with a patient I ask many important questions that not only help me come up with a diagnosis but make some suggestions that would be necessary to help the patient achieve optimal wellness.
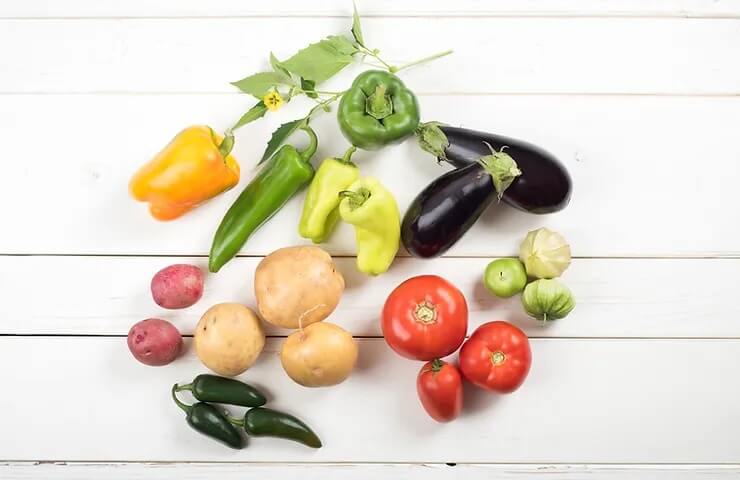
A person‘s case was presented to me. She was experiencing a great deal of joint pain to the point that it felt debilitating. This person eats healthy and practices a vegan lifestyle. She was unable to exercise due to the great amount of joint pain. This person has been to many doctors with no change in the condition. At this time I inquired about the diet. She consumed a lot of vegetables such as egg plant, white potatoes and tomatoes. At this time I stated that she could have a sensitivity to night shade vegetables.
What are Nightshade Vegetables?
Nightshade vegetables, while nutritious for many individuals, have been associated with the potential to trigger or exacerbate certain inflammatory conditions, particularly joint pain. This phenomenon is attributed to the presence of compounds called alkaloids in these vegetables. While the evidence is not conclusive and individual reactions vary, some people may experience increased inflammation and joint discomfort when consuming nightshade vegetables.
Alkaloids are natural plant compounds that serve various purposes, including defense against pests. Some individuals might be sensitive to specific alkaloids found in nightshades, leading to an exaggerated immune response and subsequent inflammation. One alkaloid in particular, solanine, has garnered attention due to its potential role in promoting inflammation in susceptible individuals.
Here’s how nightshade vegetables might contribute to inflammatory conditions such as joint pain:
-
Sensitivity to Alkaloids:
Certain individuals might be more sensitive to the alkaloids present in nightshade vegetables. These alkaloids can trigger an immune response that results in inflammation, particularly in joints. Inflammation in joints can lead to pain, stiffness, and discomfort, resembling symptoms of conditions like arthritis. -
Autoimmune Response:
Some autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, involve the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy tissues, including joints. The consumption of nightshade vegetables might exacerbate this autoimmune response in susceptible individuals, leading to increased inflammation and joint pain. -
Individual Variability:
Not everyone reacts to nightshade vegetables in the same way. Some individuals may tolerate these vegetables well without experiencing any adverse effects, while others might notice a link between their consumption and joint discomfort. -
Oxalates:
While not exclusive to nightshade vegetables, some individuals who are prone to developing calcium oxalate crystals (such as those with kidney stones) might experience joint pain if these crystals accumulate in joints. Certain nightshade vegetables, like tomatoes, contain oxalates, which could contribute to this issue.
It was reported to me that after adjusting the diet and eliminating nightshade vegetables from her diet; there was a significant reduction in joint pain. The inflammatory markers in the bloodwork reduced and she is able to exercise again and live a productive life.
It’s important to note that the relationship between nightshade vegetables and joint pain is not universally applicable. Many people consume these vegetables regularly without experiencing any adverse effects on their joints. If you suspect that nightshade vegetables might be contributing to your joint pain or inflammatory symptoms, consider the following steps:
-
Keep a Food Diary:
Monitor your diet and symptoms to identify any potential patterns between the consumption of nightshade vegetables and the onset of joint pain. -
Consult a Healthcare Professional:
If you’re experiencing persistent joint pain or inflammation, consult with a healthcare provider. They can help diagnose the cause of your symptoms and provide appropriate guidance. -
Elimination Diet:
Under the guidance of a healthcare professional or registered dietitian, you might consider temporarily eliminating nightshade vegetables from your diet to see if your symptoms improve. If they do, a controlled reintroduction can help confirm the association. -
Individualized Approach:
Nutritional needs and sensitivities vary greatly between individuals. Work with a healthcare professional to tailor your diet to your specific needs and preferences.
In conclusion, acupuncture with the addition of nutritional advice can greatly reduce painful conditions and inflammation. Learn more by scheduling an appointment with a licensed acupuncturist.